- +91 879 910 1659
- help@riderwings.org
- Mon - Sun: 9:00 - 07:00
Menu
છેલ્લો શ્વાસ
છેલ્લા શ્વાસ ની મદદ પ્રથમ શ્વાસ દ્વારા
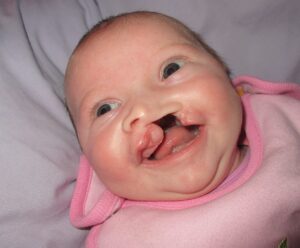
In India, more than 1.7 million children are born with birth defects every year.
In India, a country of 1.4 billion, one child is born every two seconds. But not every child survives or lives a healthy life.
A birth defect (congenital anomaly) is a health problem or an abnormal physical change that is present when a baby is born.
More than 4,000 different kinds of birth defects are reported which range from minor defects that need no treatment to serious defects that cause disabilities or require medical or surgical treatment. Of these defects in the development of brain or spinal cord, cleft lip and palate and club foot are most common.
Birth defects constitute the fifth largest cause of death in the newborn babies in our country. Globally, congenital anomalies affect 2–3% of births. In India too, 1–3 out of 100 babies are born with birth defects accounting for 27 million babies being born with birth defects each year.
Birth defects can be caused by certain genes or changes in genes. The genetic defect is inherited from either father or mother or result from sudden changes in genes called as mutations. It can also occur due to maternal exposure to drugs, chemicals, infection or radiation while the mother is pregnant or a combination of factors. However, in majority of cases (70%), the cause of birth defects is not known. Most mothers who give birth to babies with birth defects are healthy without major risk factors and have a normal pregnancy.
After birth, a newborn baby is examined in detailed to look for visible birth defects such as cleft lip, palate, open defects of the spine, defects in arms, legs, and facial features. Some others such as defects of the heart, brain, eye or internal organs, bones, and hearing loss require special tests, such as ultrasound scan, Echo scan, X-rays or hearing tests. Defects of internal organs are suspected based on external features in the baby, clinical examination findings or based on maternal history or risk factors.
Birth defects can also be detected during pregnancy. Screening tests offered in first and second trimesters of pregnancy can indirectly indicate abnormalities or ultrasound scans that can visualize structural defects. Women with risk factors and those with abnormal screening tests are offered confirmatory tests that involve taking a sample of placenta or amniotic fluid for detailed testing. Despite these tests, certain birth defects might not be diagnosed until after the baby is born.
Neural tube defects are largely preventable, unlike some other congenital defects. Folic acid (FA), a type of Vitamin B, when consumed by women before pregnancy and in early pregnancy in recommended doses, can significantly reduce the risk of spina bifida and anencephaly in newborns. Women can consume supplements or folic acid-fortified foods to obtain the recommended daily amount—400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid a day—to reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
WE CARE COUNTRY'S FUTURE
1
+
Hospitals Registered
1
+
patient registered
1
+
babies Care till date